|
|
|
A pair of generalized Polynomials which generalize the
Lucas Sequence to Polynomials is given by
![$\displaystyle {\Delta^k(x)[a^n(x)-(-1)^kb^n(x)]\over\Delta(x)}$](l2_1088.gif) |
(1) | ||
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
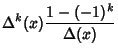 |
(6) | ||
| (7) |
| (8) | |||
| (9) |
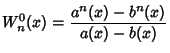 |
(10) | ||
| (11) |
| Polynomial 1 | Polynomial 2 | ||
| 1 | Fibonacci |
Lucas |
|
| 1 | Pell |
Pell-Lucas |
|
| 1 | Jacobsthal |
Jacobsthal |
|
| Fermat
|
Fermat-Lucas |
||
| Chebyshev Polynomial of the Second Kind |
Chebyshev Polynomial of the First Kind |
See also Lucas Sequence
References
Horadam, A. F. ``Extension of a Synthesis for a Class of Polynomial Sequences.'' Fib. Quart. 34,
68-74, 1996.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein