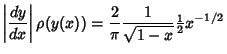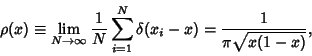With 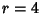 , the Logistic Equation becomes
, the Logistic Equation becomes
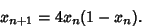 |
(1) |
Now let
![\begin{displaymath}
x\equiv \sin^2({\textstyle{1\over 2}}\pi y) = {\textstyle{1\over 2}}[1-\cos(\pi y)]
\end{displaymath}](l2_820.gif) |
(2) |
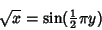 |
(3) |
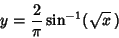 |
(4) |
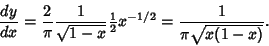 |
(5) |
Manipulating (2) gives
so
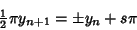 |
(7) |
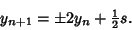 |
(8) |
But ![$y\in [0,1]$](l2_829.gif) . Taking
. Taking ![$y_n\in[0,1/2]$](l2_830.gif) , then
, then 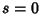 and
and
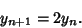 |
(9) |
For ![$y\in [1/2,1]$](l2_833.gif) ,
, 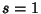 and
and
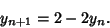 |
(10) |
Combining
![\begin{displaymath}
y_n=\cases{
2y_n & for $y_n \in [0,{\textstyle{1\over 2}}]$\cr
2-2y_n & for $y_n \in [{\textstyle{1\over 2}},1]$,\cr}
\end{displaymath}](l2_836.gif) |
(11) |
which can be written
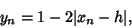 |
(12) |
the Tent Map with 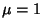 , so the Natural Invariant in
, so the Natural Invariant in 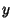 is
is
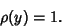 |
(13) |
Transforming back to 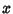 gives
gives
This can also be derived from
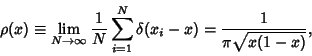 |
(15) |
where 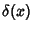 is the Delta Function.
is the Delta Function.
See also Logistic Equation
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-25
![]() , the Logistic Equation becomes
, the Logistic Equation becomes