|
|
|
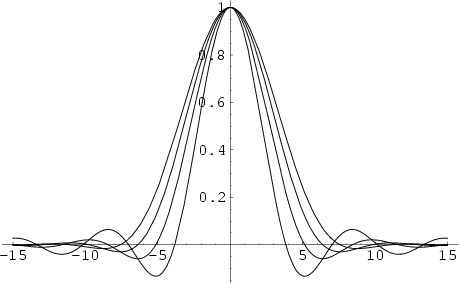
The lambda function defined by Jahnke and Emden (1945) is
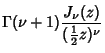 |
(1) | ||
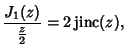 |
(2) |
A two-variable lambda function defined by Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (1979) is
| (3) |
See also Airy Functions, Dirichlet Lambda Function, Elliptic Lambda Function, Jinc Function, Lambda Hypergeometric Function, Mangoldt Function, Mu Function, Nu Function
References
Gradshteyn, I. S. and Ryzhik, I. M.
Tables of Integrals, Series, and Products, 5th ed. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, p. 1079, 1979.
Jahnke, E. and Emde, F. Tables of Functions with Formulae and Curves, 4th ed. New York: Dover, 1945.