|
|
|
There are several types of integrals which go under the name of a ``Dirichlet integral.'' The integral
| (1) |
The integral
| (2) |
Another integral is denoted
| (3) |
There are two types of Dirichlet integrals which are denoted using the letters ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The type 1 Dirichlet
integrals are denoted
. The type 1 Dirichlet
integrals are denoted ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , and the type 2 Dirichlet integrals are denoted
, and the type 2 Dirichlet integrals are denoted ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
The type 1 integrals are given by
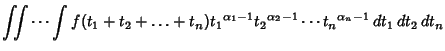 |
|||
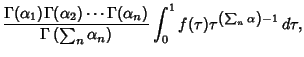 |
(4) |
| (5) |
The type 2 integrals are given for ![]() -D vectors
-D vectors ![]() and
and ![]() , and
, and ![]() ,
,
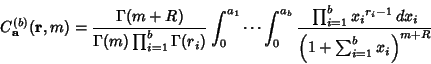 |
(6) |
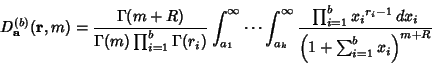 |
(7) |
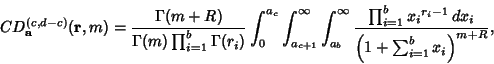 |
(8) |
| (9) | |||
| (10) |
|
|
|
|
|
(11) |
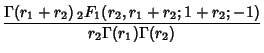 |
(12) | ||
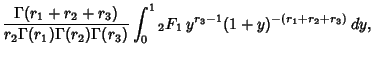 |
(13) |
| (14) |
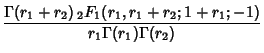 |
(15) | ||
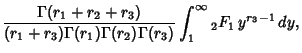 |
(16) |
| (17) |
References
Sobel, M.; Uppuluri, R. R.; and Frankowski, K.
Selected Tables in Mathematical Statistics, Vol. 4: Dirichlet Distribution--Type 1. Providence, RI: Amer. Math. Soc., 1977.
Sobel, M.; Uppuluri, R. R.; and Frankowski, K.
Selected Tables in Mathematical Statistics, Vol. 9: Dirichlet Integrals of Type 2 and Their Applications.
Providence, RI: Amer. Math. Soc., 1985.
![]() Weisstein, E. W. ``Dirichlet Integrals.'' Mathematica notebook DirichletIntegrals.m.
Weisstein, E. W. ``Dirichlet Integrals.'' Mathematica notebook DirichletIntegrals.m.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein