|
|
|
A Sufficient condition on the Lindeberg-Feller Central Limit Theorem. Given random variates ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
..., let
,
..., let
![]() , the Variance
, the Variance ![]() of
of ![]() be finite, and Variance of the distribution
consisting of a sum of
be finite, and Variance of the distribution
consisting of a sum of ![]() s
s
| (1) |
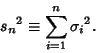 |
(2) |
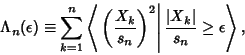 |
(3) |
| (4) |
See also Feller-Lévy Condition
References
Zabell, S. L. ``Alan Turing and the Central Limit Theorem.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 102, 483-494, 1995.