|
|
|
Also called ``the'' Gaussian Quadrature or Legendre Quadrature. A Gaussian Quadrature over the
interval ![]() with Weighting Function
with Weighting Function ![]() . The Abscissas for quadrature order
. The Abscissas for quadrature order ![]() are
given by the roots of the Legendre Polynomials
are
given by the roots of the Legendre Polynomials ![]() , which occur symmetrically about 0.
The weights are
, which occur symmetrically about 0.
The weights are
| (1) |
| (2) |
![$\displaystyle {[2(n+1)]!\over 2^{n+1}[(n+1)!]^2} {2^n(n!)^2\over (2n)!}$](l1_1320.gif) |
|||
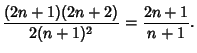 |
(3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
| (7) |
| (8) |
| 2 | ± 0.57735 | 1.000000 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.888889 |
| ± 0.774597 | 0.555556 | |
| 4 | ± 0.339981 | 0.652145 |
| ± 0.861136 | 0.347855 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0.568889 |
| ± 0.538469 | 0.478629 | |
| ± 0.90618 | 0.236927 |
The Abscissas and weights can be computed analytically for small ![]() .
.
| 2 |
|
1 |
| 3 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
References
Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 28th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 462-463, 1987.
Chandrasekhar, S. Radiative Transfer. New York: Dover, pp. 56-62, 1960.
Hildebrand, F. B. Introduction to Numerical Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 323-325, 1956.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein