|
|
|
An ![]() -step Fibonacci sequence is given by defining
-step Fibonacci sequence is given by defining ![]() for
for ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and
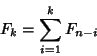 |
(1) |
The limit
![]() is given by solving
is given by solving
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
See also Fibonacci Number, Tribonacci Number
References
Sloane, N. J. A. Sequences
A000045/M0692,
A000073/M1074, and
A000078/M1108
in ``An On-Line Version of the Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.''
http://www.research.att.com/~njas/sequences/eisonline.html and Sloane, N. J. A. and Plouffe, S.
The Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. San Diego: Academic Press, 1995.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein