|
|
|
In response to a letter from Goldbach, Euler ![]() considered Double Sums of the form
considered Double Sums of the form
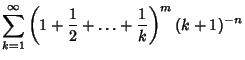 |
(1) | ||
![$\displaystyle \sum_{k=1}^\infty [\gamma+\psi_0(k+1)]^m (k+1)^{-n}$](e_2371.gif) |
(2) |
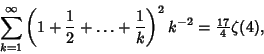 |
(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4) |
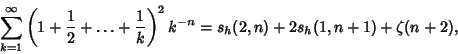 |
(5) |
Bailey et al. (1994) subsequently considered sums of the forms
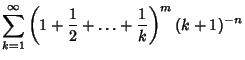 |
(6) | ||
![$\displaystyle \sum_{k=1}^\infty \left[{1-{1\over 2}+\ldots+{(-1)^{k+1}\over k}}\right]^m (k+1)^{-n}$](e_2387.gif) |
(7) | ||
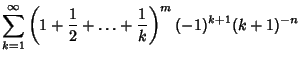 |
(8) | ||
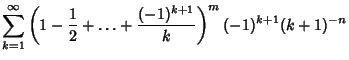 |
|||
| (9) | |||
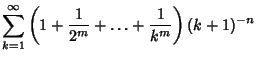 |
(10) | ||
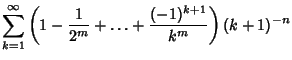 |
(11) | ||
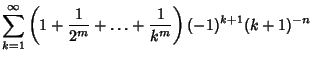 |
(12) | ||
| (13) | |||
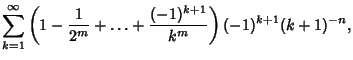 |
|||
| (14) |
where ![]() and
and ![]() have the special forms
have the special forms
![$\displaystyle \sum_{k=1}^\infty [\gamma+\psi_0(n+1)]^m {k+1}^{-n}$](e_2402.gif) |
(15) | ||
![$\displaystyle \sum_{k=1}^\infty \{\ln 2+{\textstyle{1\over 2}}(-1)^n[\psi_0({\t...
...2}}n+{\textstyle{1\over 2}})-\psi_0({\textstyle{1\over 2}}n+1)]\}^m (k+1)^{-m}.$](e_2404.gif) |
(16) |
|
|
(17) |
|
|
|
|
|
(18) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(19) |
|
|
(20) |
|
|
|
|
|
(21) |
|
|
|
|
|
(22) |
|
|
|
|
|
(23) |
where ![]() is a Binomial Coefficient. Explicit formulas inferred using the PSLQ Algorithm include
is a Binomial Coefficient. Explicit formulas inferred using the PSLQ Algorithm include
| (24) | |||
| (25) | |||
| (26) | |||
| (27) | |||
| (28) | |||
| (29) | |||
| (30) | |||
| (31) | |||
| (32) | |||
| (33) | |||
| (34) | |||
| (35) | |||
| (36) | |||
| (37) | |||
| (38) |
| (39) | |||
| (40) | |||
| (41) |
| (42) | |||
| (43) | |||
| (44) |
| (45) | |||
| (46) | |||
| (47) |
References
Bailey, D. and Plouffe, S. ``Recognizing Numerical Constants.''
http://www.cecm.sfu.ca/organics/papers/bailey/.
Bailey, D. H.; Borwein, J. M.; and Girgensohn, R. ``Experimental Evaluation of Euler Sums.'' Exper. Math.
3, 17-30, 1994.
Berndt, B. C. Ramanujan's Notebooks: Part I. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1985.
Borwein, D. and Borwein, J. M. ``On an Intriguing Integral and Some Series Related to
Borwein, D.; Borwein, J. M.; and Girgensohn, R. ``Explicit Evaluation of Euler Sums.''
Proc. Edinburgh Math. Soc. 38, 277-294, 1995.
de Doelder, P. J. ``On Some Series Containing
![]() .''
Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 123, 1191-1198, 1995.
.''
Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 123, 1191-1198, 1995.
![]() and
and
![]() for Certain Values
of
for Certain Values
of ![]() and
and ![]() .'' J. Comp. Appl. Math. 37, 125-141, 1991.
.'' J. Comp. Appl. Math. 37, 125-141, 1991.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein